
POLYSIS is specifically designed to be used after a researcher or technician has performed an IGC experiment using a prepared column within a laboratory setting.
There are two programs offered:
1. The calculations of the interaction of 37 solvents with polymers and materials in terms of the interaction coefficient known as “CHI” (χ12). The coefficients of solvent-material system cannot be obtained unless there is a database available with the critical data related to the physical properties of the materials. The software has a database which is comprised of a set of Antoine constants of 37 solvents collected from the literature. Antoine constants are vital to the calculation of saturated vapor pressure, liquid and vapor densities of solvents used in a series of equations. The software combines the parameters obtained from the gas chromatography experiment and the stored database of solvents in the software to create a new database which enables the calculation of the solvent-material system interactions (χ12). The software provides a user-friendly, window-based interface, as shown below.
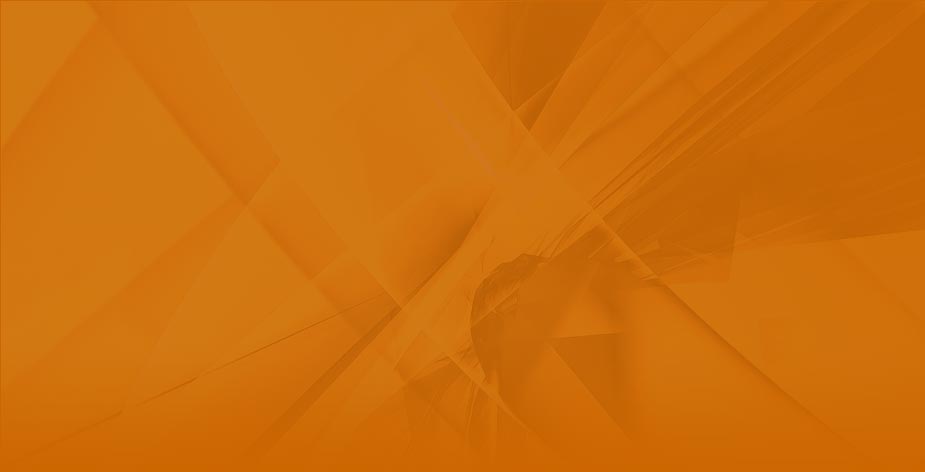
Here is the input page of parameters obtained from gas chromatography:
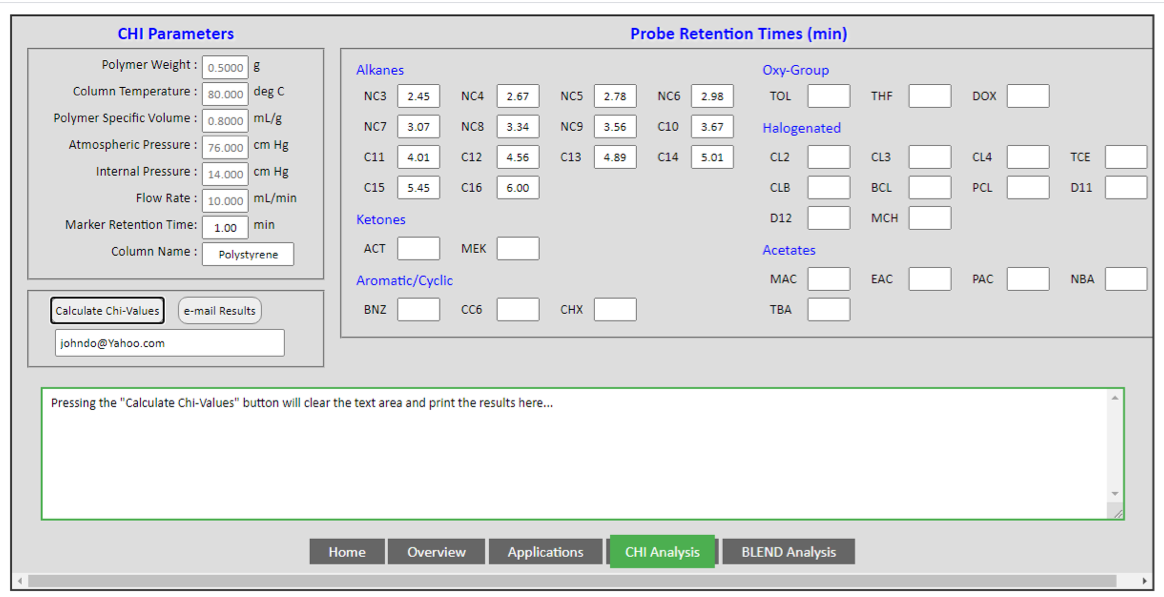 Solvents are arranged by their chemical nature as families: alkanes, acetates, ether and keto group, cyclic and aromatics and chlorinated solvents. Each solvent is assigned a code, which are collectively summarised in this table. Once the chromatographic conditions are entered into the left column, and the retention time of each solvent is entered into the right column, by clicking the “calculate” tab, the output of the results appears in the lower half of the screen, as shown in the following figure. The calculations and final report can easily be exported to Excel for further manipulation of the data.
Solvents are arranged by their chemical nature as families: alkanes, acetates, ether and keto group, cyclic and aromatics and chlorinated solvents. Each solvent is assigned a code, which are collectively summarised in this table. Once the chromatographic conditions are entered into the left column, and the retention time of each solvent is entered into the right column, by clicking the “calculate” tab, the output of the results appears in the lower half of the screen, as shown in the following figure. The calculations and final report can easily be exported to Excel for further manipulation of the data.
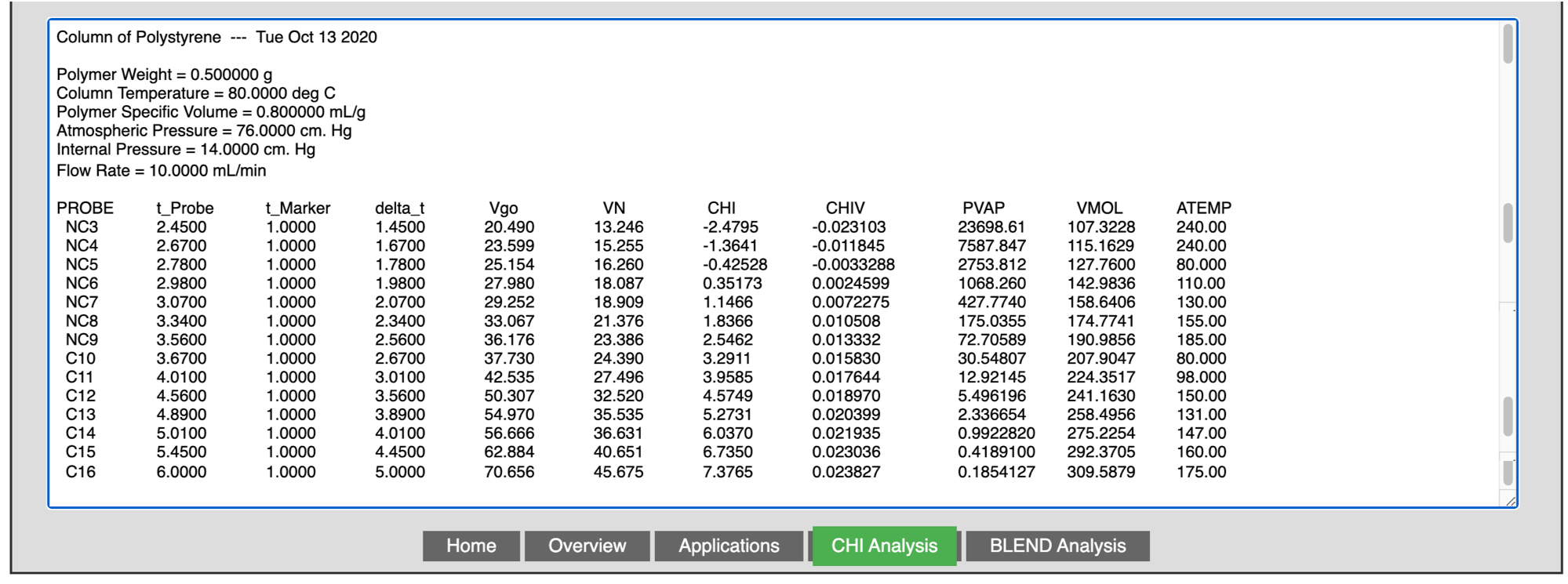
POLYSIS provides researchers and industrial end users with a time efficient way to determine the solubility and the strength of the interaction of 37 solvents with materials. It also has numerous applications in data analysis of thermodynamic parameters of materials using the measured chromatographic quantities such as retention time of marker and solvent, head pressure, carrier gas flow rate, oven temperature and the atmospheric pressure. The thermodynamic parameters provided by POLYSIS help characterize the properties of the materials. Using this program it can be determined whether the solvent-material system is endothermic or exothermic. The CHI values from this program can also be used to explore the effect of temperature and the chemical nature of the solvents used in the interactions of the solvent-material system. The CHI parameter feature compares the strength of interactions of materials to 37 solvents to determine the interaction between the material and solvent.
2. The second program of POLYSIS offered is the characterization of a Blend (a pair of polymers or materials). This feature provides information about the interaction between the two materials as an interaction parameter (χ23). This feature determines whether the two materials are compatible with each other by determining whether the miscibility of the blend is endothermic or exothermic over a range of temperatures and weight fractions.
To use this feature, the end user has to prepare and study three chromatographic columns at identical conditions as follows:
The information on the characteristics of the blend such as name, temperature, weight of both polymers, and specific volume of each polymer are entered once in the left hand side of the window. The retention times for each solvent obtained from the three chromatographic columns (Polymer 2, Polymer 3, and Blend) are entered in the corresponding tabs on the right hand side of the window.
The following three figures show the characteristics of the blend, and the solvent retention times for polymer 2, polymer 3, and the resulting blend:
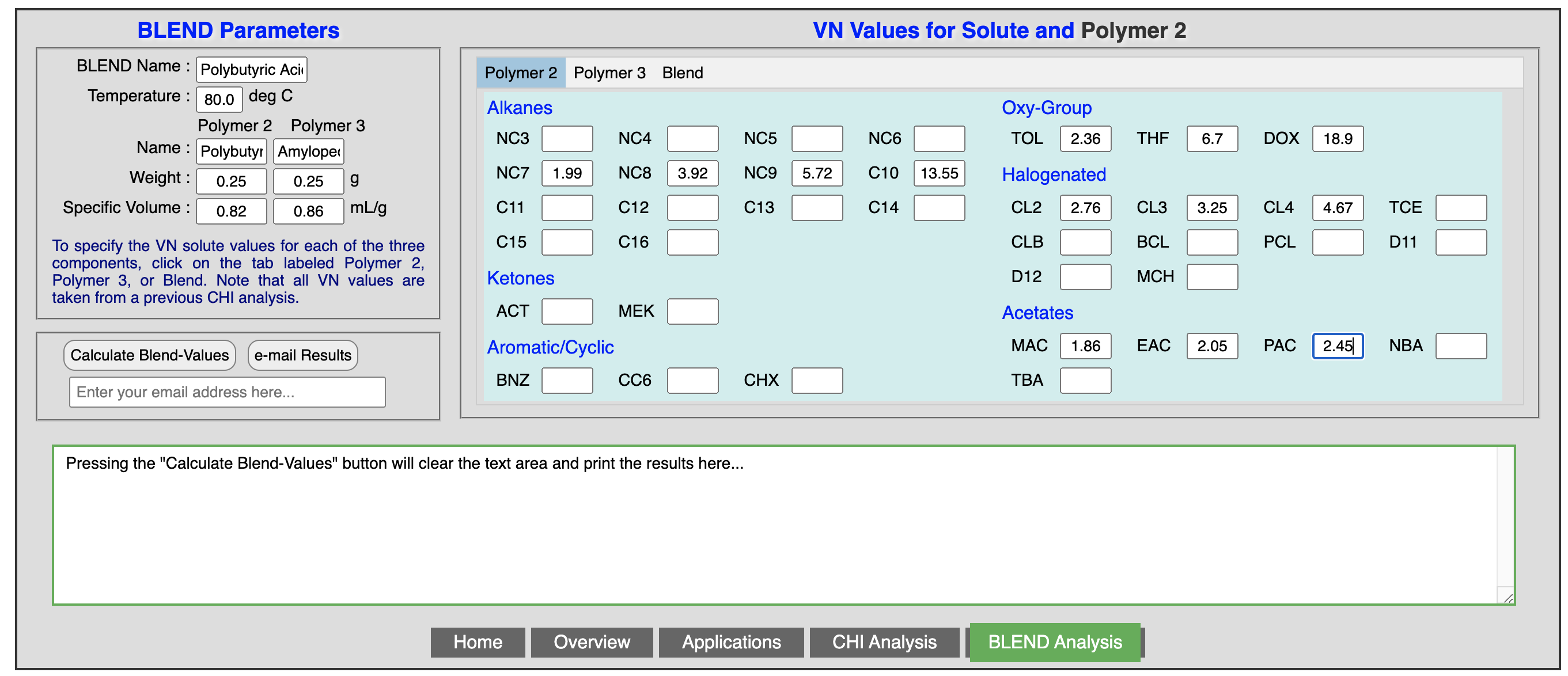
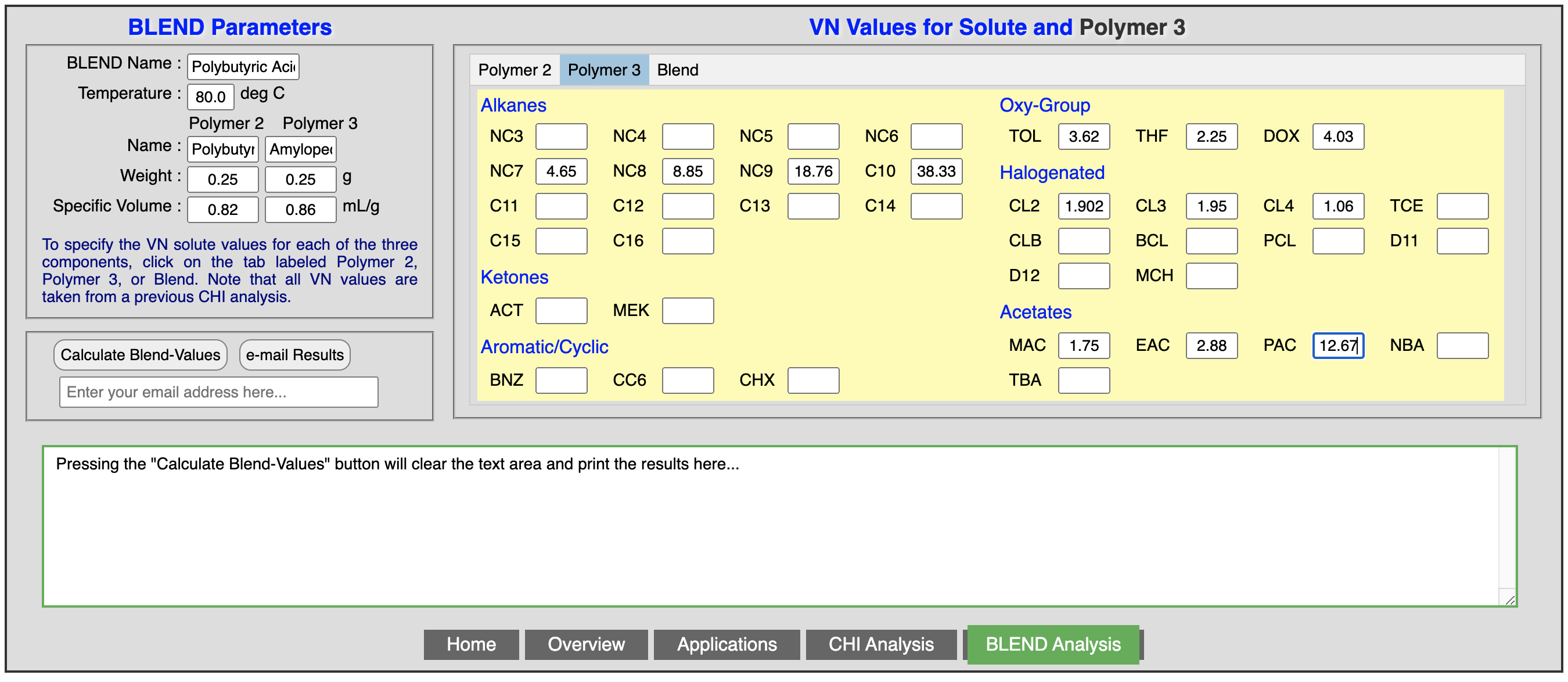
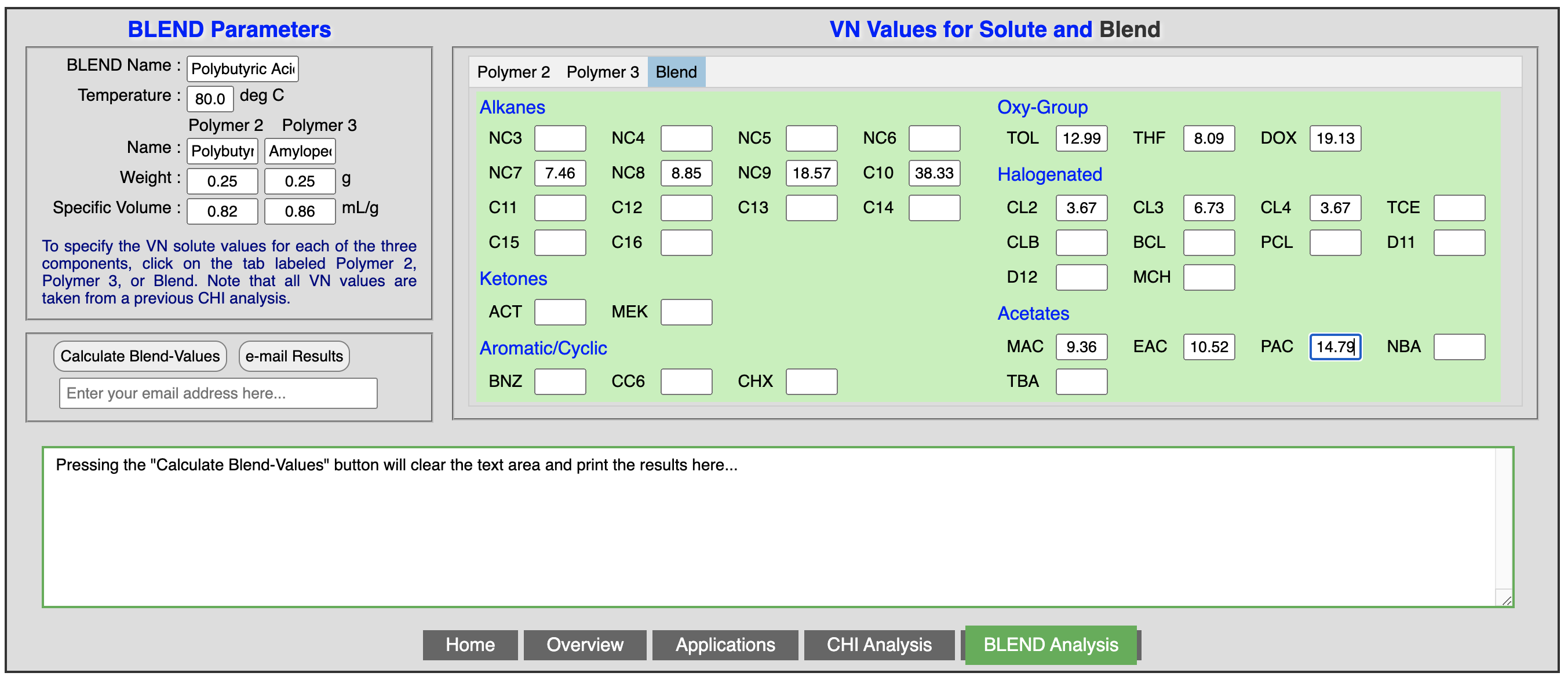
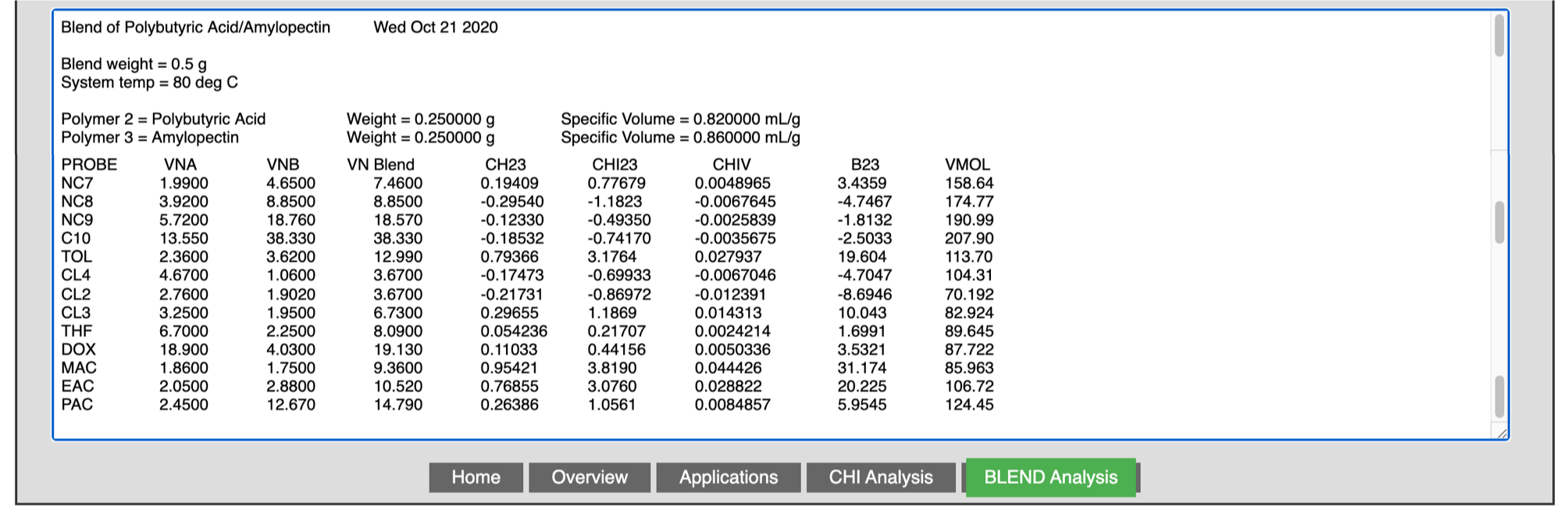
Once all the parameters are entered, clicking the “calculate” tab will show the output of the results in the lower part of the window, as shown in the following figure. The results can be exported to Excel, highlighted and copied to a note book, or e-mailed to your account.
Blend’s output
Our technology addresses the problem of requiring time consuming experiments and calculations by the automation of the data collected from the gas chromatography experiments and subjected to the desired calculations needed for further exploration of the physico-chemical properties of polymers. Further, our technology’s value proposition is to provide users an intuitive software which saves time and money.
The software is under development and will be launched soon. For more information about the services offered and prices, please contact us at: polysis@buffalostate.edu
For further information, please contact us.
POLYSIS:Software for Thermodynamic Chemical Analysis of Materials
Some content on this page is saved in PDF format. To view these files, download Adobe Acrobat Reader free. If you are having trouble reading a document, request an accessible copy of the PDF or Word Document.
